Week 11: Visulization of Spatio-Temporal Data (Optional)
1 Introduction
- In Lab 11, we follow Lab 2.2 of Spatio-Temporal Statistics with
R. You can download the electronic pdf through https://spacetimewithr.org/.
- In this document, I will only highlight some important points; that is, the visulization of spatio-temporal data.
2 Spatial Plots
- First, we load the dataset.
- z: temperature (F)
- id: weather station ID.
- t: the same as the column day
- We do not really used column julian nor proc
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(sf)
load("datasets/Tmax.Rdata")
head(Tmax)## julian year month day id z proc lat lon date t
## 1 728050 1993 5 1 3804 82 Tmax 39.35 -81.43333 1993-05-01 1
## 2 728051 1993 5 2 3804 84 Tmax 39.35 -81.43333 1993-05-02 2
## 3 728052 1993 5 3 3804 79 Tmax 39.35 -81.43333 1993-05-03 3
## 4 728053 1993 5 4 3804 72 Tmax 39.35 -81.43333 1993-05-04 4
## 5 728054 1993 5 5 3804 73 Tmax 39.35 -81.43333 1993-05-05 5
## 6 728055 1993 5 6 3804 78 Tmax 39.35 -81.43333 1993-05-06 6- Next, the plot will be produced by package ggplot2. The new
function here
- geom_path: add US states map. You can replace these US map with Australia ones from Week 7 Lab.
- facet_grid(~date): for each date (1, 15 and 30), produce a plot.
Tmax_1 = Tmax %>% filter(t %in% c(1, 15, 30)) # extract data
# Spatial Plots
NOAA_plot <- ggplot(Tmax_1) + # plot points
geom_point(aes(x = lon,y = lat, # lon and lat
colour = z), # attribute color
size = 1.2) + # point size
scale_colour_gradientn(name = "degF", # attach color scale
colours = terrain.colors(10)) +
xlab("Longitude (deg)") + # x-axis label
ylab("Latitude (deg)") + # y-axis label
geom_path(data = map_data("state"), # add US states map
aes(x = long, y = lat, group = group)) +
coord_fixed(1.3) +
facet_grid(~date) + # facet by time
coord_fixed(xlim = c(-105, -75),
ylim = c(25, 50)) + # zoom in
theme_bw()
NOAA_plot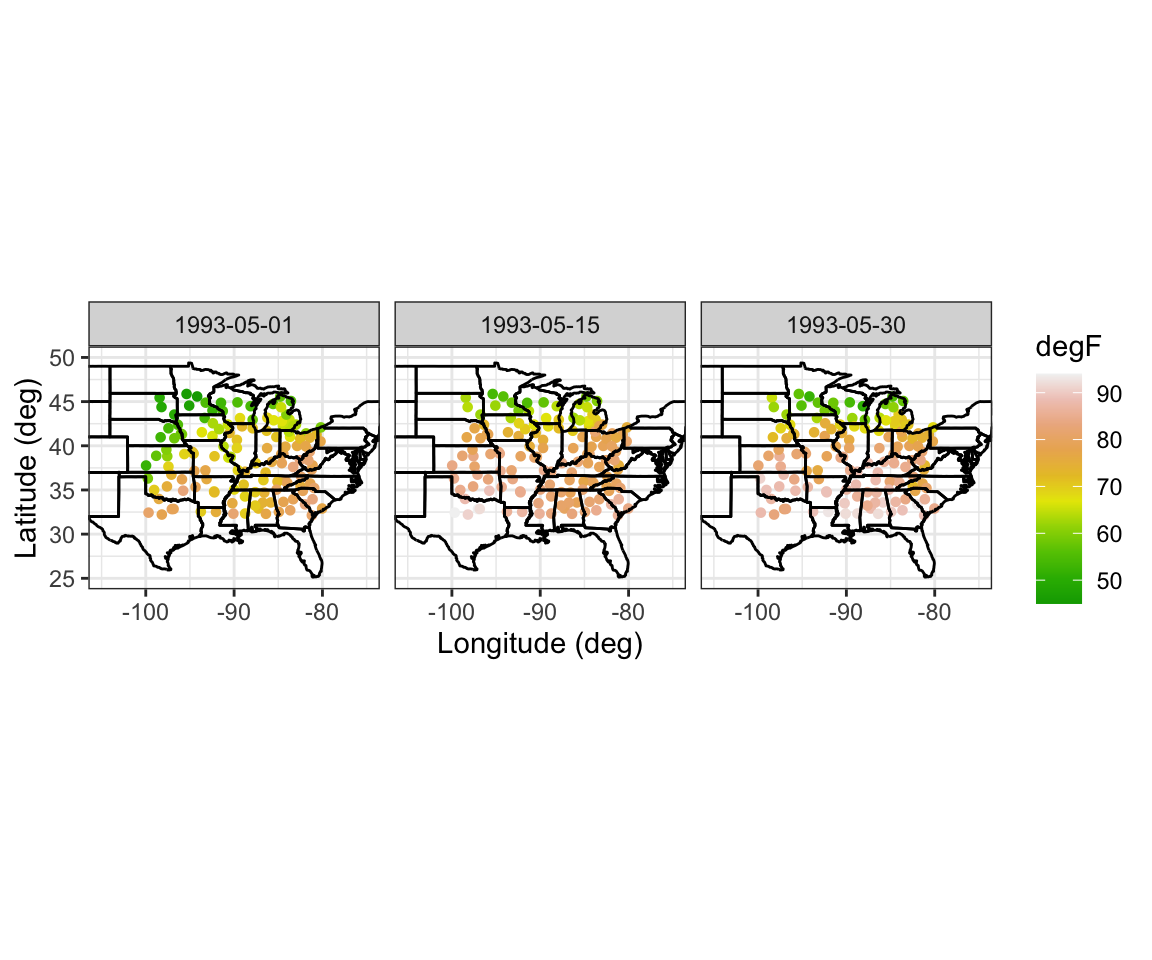
We can also use sf object from Lab 5 and Lab 6 to achieve the same results
First, transform the data to sf object using the function st_as_sf. Here, 4326 is WGS 84, which is the longitude and latitude.
state_sf = st_as_sf(maps::map("state", plot = FALSE, fill = TRUE),
crs = st_crs(4326))
Tmax_1sf = st_as_sf(Tmax_1, coords = c("lon", "lat"), crs = st_crs(4326))Next, visualise the data using geom_sf
NOAA_plot2 = ggplot() + geom_sf(data = state_sf) +
geom_sf(data = Tmax_1sf, aes(color = z)) +
coord_sf(xlim = c(-105, -75), ylim = c(25, 50)) +
scale_colour_gradientn(name = "degF", colours = terrain.colors(10)) +
facet_grid(~date)
NOAA_plot2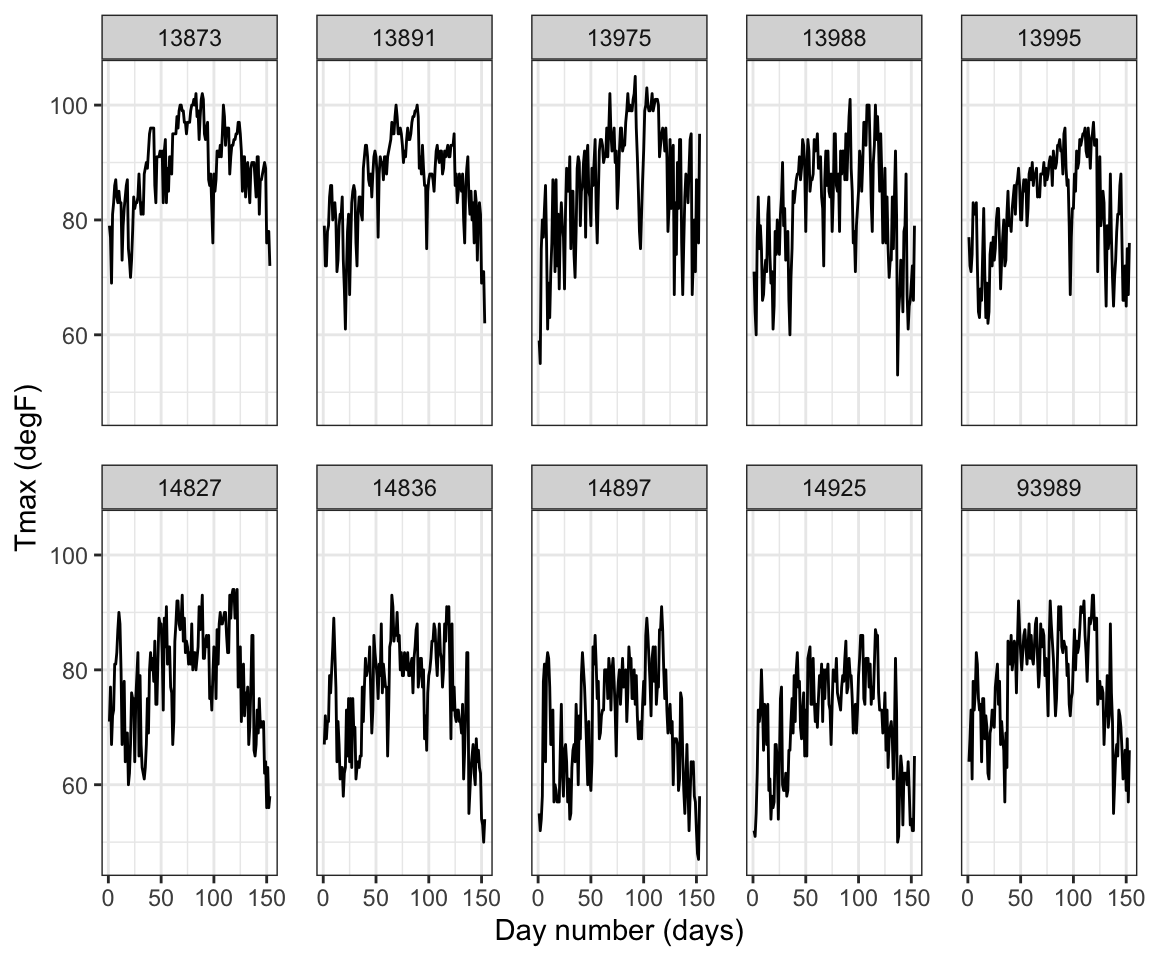
3 Time-Series Plots
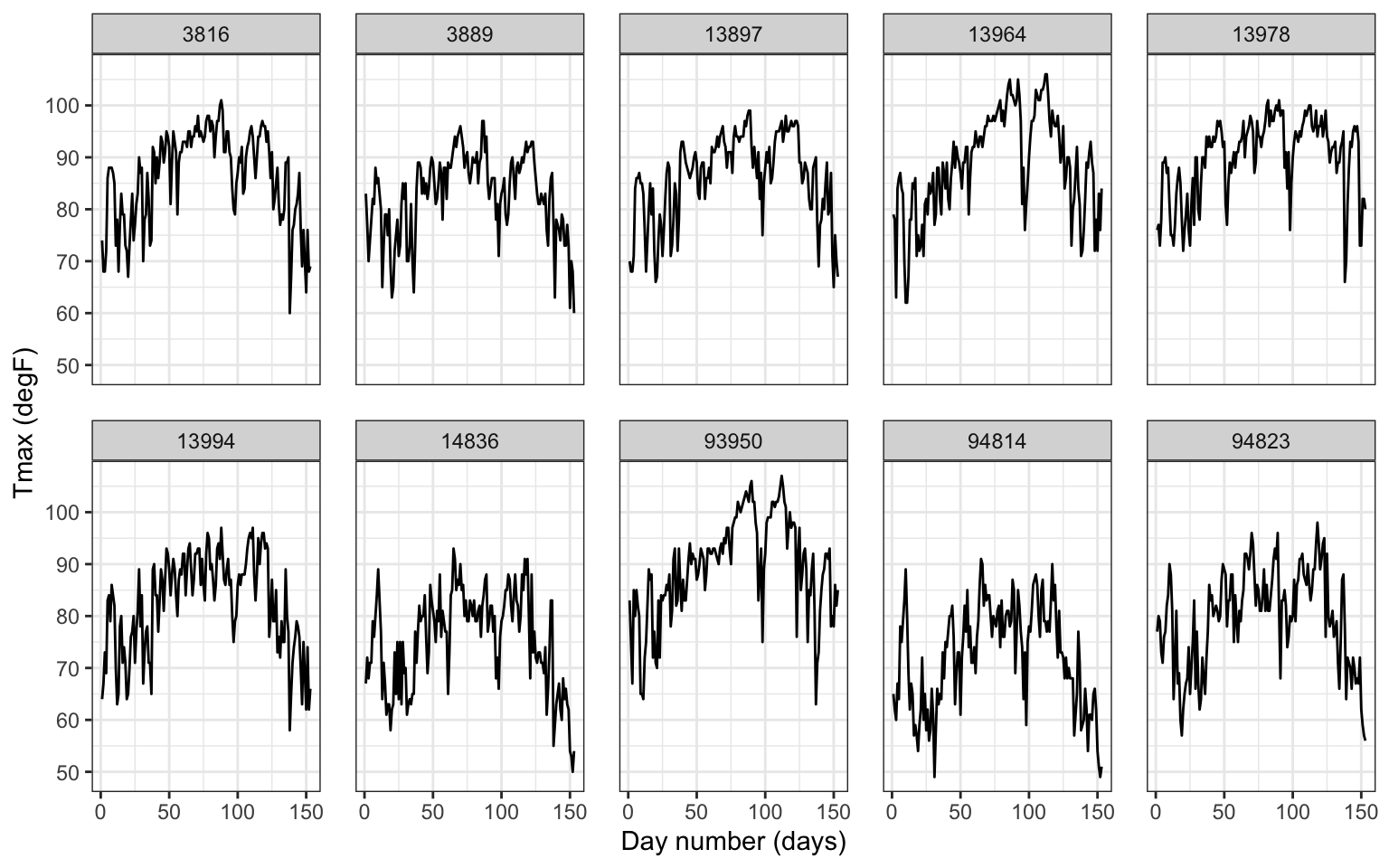
First, we randomly select 10 station for visualization.
UIDs <- unique(Tmax$id) # extract IDs
UIDs_sub <- sample(UIDs, 10) # sample 10 IDs
Tmax_sub <- filter(Tmax, id %in% UIDs_sub) # subset data
head(Tmax_sub)## julian year month day id z proc lat lon date t
## 1 728050 1993 5 1 3816 74 Tmax 37.06667 -88.76667 1993-05-01 1
## 2 728051 1993 5 2 3816 68 Tmax 37.06667 -88.76667 1993-05-02 2
## 3 728052 1993 5 3 3816 68 Tmax 37.06667 -88.76667 1993-05-03 3
## 4 728053 1993 5 4 3816 72 Tmax 37.06667 -88.76667 1993-05-04 4
## 5 728054 1993 5 5 3816 86 Tmax 37.06667 -88.76667 1993-05-05 5
## 6 728055 1993 5 6 3816 88 Tmax 37.06667 -88.76667 1993-05-06 6Next, time-series is plotted.
## ------------------------------------------------------------------------
TmaxTS <- ggplot(Tmax_sub) +
geom_line(aes(x = t, y = z)) + # line plot of z against t
facet_wrap(~id, ncol = 5) + # facet by station
xlab("Day number (days)") + # x label
ylab("Tmax (degF)") + # y label
theme_bw() + # BW theme
theme(panel.spacing = unit(1, "lines")) # facet spacing: the space between each subplots.
TmaxTS